Advantages and benefits of steel rings
Advantages of steel rings
In the past, primarily alloyed gray iron or nodular iron was used as piston ring material in gasoline or diesel engines. Today, steel is being used more and more by engine designers. Steel rings have been used for over 30 years in the truck sector, e.g. at Mercedes-Benz.
The resulting good experience and technical progress in the processing of this material have contributed, among other things, to the widespread use of steel material in all areas of today’s engine technology.
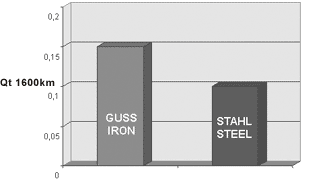
Oil consumption and blow-by rate
The smaller cross-section of the steel ring improves the ring’s mold filling capacity. As a result, the ring follows the deformations of the cylinder surface and thus ensures more efficient sealing.
Why steel?
Today’s engines place higher demands on piston rings. Thermal and mechanical stress is increasing significantly. Additional restrictions on emissions are further demands on the precision of engine components. All these factors have created the need for a material that must be stronger and harder than those previously used. Better sealing, resistance to fracture and wear under load are also required. Steel brings the suitable properties. Different steel materials are used, depending on the requirements of the engine. Retrofitting during engine overhauls is possible at any time without any problems.
Steel ring vs. nodular cast iron ring
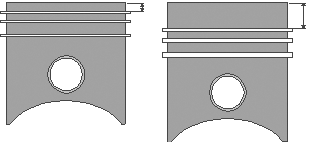
In newer engines, the lower axial ring height of steel rings allows them to be placed even closer to the piston crown, thus reducing exhaust emissions.
Reduction of oil consumption
The use of steel in the design of a piston ring allows a reduction in the axial ring height and additionally in the radial wall thickness. The ring, which is thus much lighter, has the ability of better sealing of the ring groove, but at the same time the stress of the ring is proportionally much higher compared to the cast ring. This results in better adaptation to slightly out-of-round cylinders. This also means that normally occurring oil consumption is thus contained or reduced.
Lower exhaust emissions
When designing pistons for new engines, the strength of the steel allows the first ring groove to be placed closer to the piston crown to achieve a reduction in exhaust emissions. This design reduces the gap volume at the firewall. Fewer unburned particles in diesel engines and fewer hydrocarbons in gasoline engines are the result.
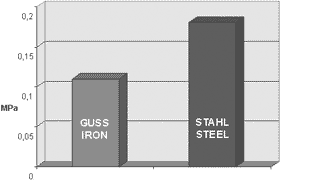
Elongation strength
Only steel compression rings can guarantee the elongation strength, hardness, and fatigue containment that are absolutely necessary for today’s engines.
The strength of steel
Compared to ductile or gray iron, steel is characterized by the fact that there is no possibility of ring fracture. Due to the greater hardness of steel, there are also advantages over cast materials in terms of flank wear of the rings and groove wear of the piston. This applies to both diesel and gasoline engines. Many years of practical experience have sufficiently confirmed this.
Flank wear
Steel rings ensure a longer service life and reduce groove wear of the piston.
Steel material piston rings
Advantages:
- Higher tangential force
- Higher mileage
- Greater hardness
- Lower ring heights
- Greater fatigue life
Benefits:
- More resistant to load
- Reduction of flank wear
- Reduction of groove wear
- Longer maintenance intervals
- Better adaptation to the cylinder
- Reduction of oil consumption
- Reduction of the blow-by quantity (Blow-By)
- Less friction
NPR of Europe GmbH assumes no liability for the completeness and correctness of the information in this report. It is exclusively the responsibility of the customer to inquire about the properties of the material and its usability for the use intended by the customer. NPR of Europe GmbH also points out that all information in this report does not legally represent a guarantee of quality or a warranty of properties.